<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-7467848586067900"
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
Climate and Science Reporter, BBC News
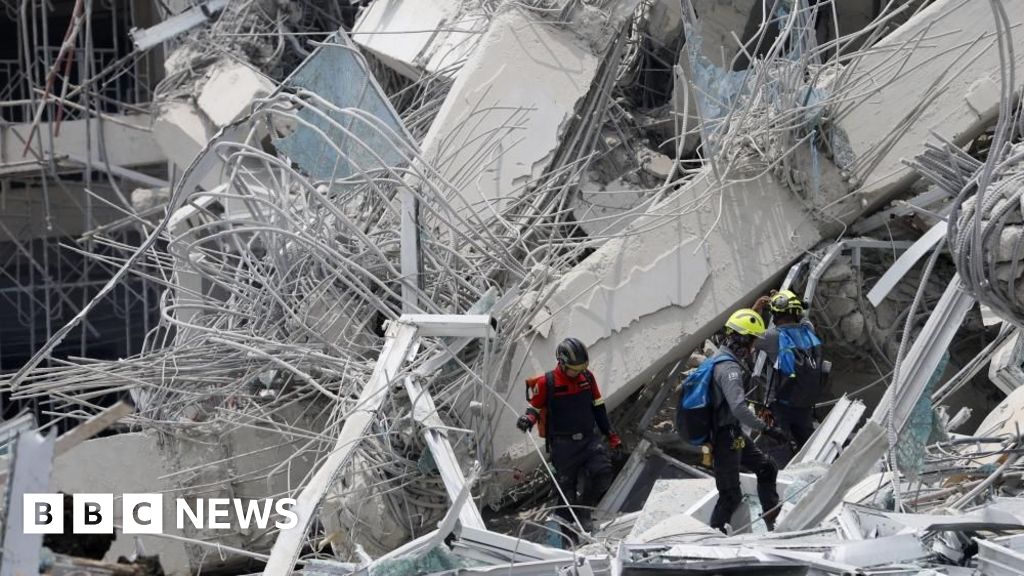
A Major Earthquake in Myanmar on Friday has caused more than 2,000 deaths and led to the collapse of numerous structures.
Even Though The South-East Asian Nation is a High Risk Region Earthquakes, Neighbouring Thailand and China – What Were Also affected by The Quake – Not Not Not.
The Thai Capital, Bangkok, moth 1,000km (621 miles) from the Epicentre of the Earthquake – And Yet an unfinished High-Rise Building in The City Was by It.
Here we will explain what caused this earthquake, and how he was a mighty to have a powerful effect So far Away.
What caused the earthquake?
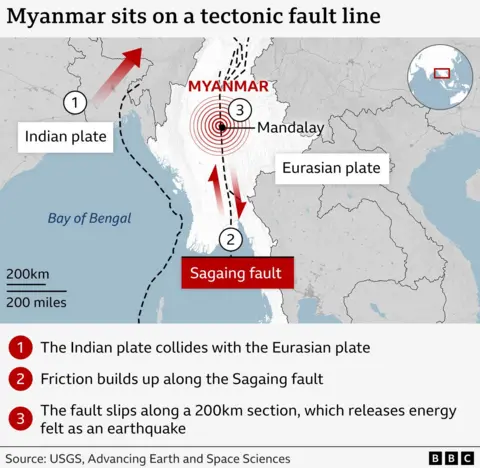
The Earth’s Upper Layer is Split Into Different Sections, Called Tectonic Plates, WHICH ARE ALL MOVING CONSTATELY. Someone Move Acher Other, Whilst Others Are Above And Below Each.
It is this Movement That Causes Earthquakes and Volcanoes.
Myanmar is considered the most geologically “Active” Areas in The World’s Because Of The Top Of The Converge Of Four of These Plates – The Indian Plate, The Indian Plate and The Burma Microplate.
The Himalayas Were Formed by The Indian Plate Colliding With The Eurasian Plate, and The 2004 Tsunami As A Result Of The Indian Plate Burma Microplate.
Dr. Rebecca Bell, A Reader Imperial College London, Said That to Accommodate All Of Thi Motion, Faults – Cracks in the Rock – Form Wrich Allow Tectonic Plates to “Slither” Sideways.
There is a Major Fault Called The Sagaing Fault, Which Cuts Right Thought Myanmar North to South And More Than 1,200km (746 Miles) Long.
Early date Suggests That The Movement That Caused 7.7-Magnitude Earthquake Was a “Strike-Slip” – Where Two Blocks Move Horizontally Along Echer.
This Aligns With The Movement Typical of the Saging Fault.
As the Plates Move Past Ether, they can betome Stuck, Building Friction Until It Is Suddenly Released And The Earth Shifts, Causing An Earthquake.
Why The Earthquake Felt So Far Away?
Earthquakes Can Happen at Up to 700km (435 Miles) Below The Surface. This One Was Just 10km From The Surface, Making It Very Shallow. This Increases The Amount of Shaking at The Surface.
The Earthquake Was Also Very Large – Measuring 7.7 The Moment Scale. It produced more energy than the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima, According to the US Geological Survey.
The Size Of The Quake Was Because of the Type of Fault, Said Dr Bell.
“The Straight Nature (of the Fault) Means Earthquakes Can Rupture Over Large Areas – and The Larger The Fault That Slips, The Larger The Earthquake,” She Explained.
“There Have Six Magnitude 7 or Greater Earthquakes in this Region in the Last Century.”
This Straight Fault Also Means A Lot Of The Energy Can Be Carried Down Its Length – What Extends for 1,200km South Towards Thailand.
When it is comes to the Earth Shook So Much, The Quake Was It Rare “Super Shear” – Meaning Energy from The Rupture In The Earth’s Faster Than Seismic Waves Can Travel Through The Earth.
Seismologist Prof Frederik Tilmann, From The Helmholtz Center in Germany, Explained in Analysis Online at A 5km per second – Making It’s Supersonic Jet “.
Because The Fracture “Unzipped” The South, Also Directed This Piled Up Energy Towards The Thai Capital, Bangkok, And This Is Why The Earthquake Had Such An Impact So Far Away.
How Earthquakes Are Felt at The Surface Is Also Determined by The Type Of.
In Soft Soil – What is Bangkok Is Built on – Seismic Waves (The Vibrations of the Earth) Slow Down and Build Up, Getting Bigger in Size.
So, Bangkok’s Geology Would Have Made The Ground Shaking More Intense.
Why did you just have one skyscraper collapse in Bangkok?
While Dramatic Footage has emerged of High-Rise Buildings in Bangkok Swaying During The Quake – Knocking Water From Rooftop Pools – The unfinished headquarters for the auditor-general’s Office Bangkok’s Chatuches District Appears to Be The Only Skyscraper to Collapse.
Prior to 2009, Bangkok Did Not Have A Comprehensive Safety Standard Buildings To Withstand Earthquakes, According to Dr. Christian Málaga-Chuquitaype, A Senior Lecturer in Earthquake Engineering in Imperial College London.
This Means That Older Buildings Would Have Be Particularly Vulnerable.
This is not unusual, as Earthquake-resistant buildings can be more expensive to construct and thailand, unlike Myanmar, Does Not Frequently Experience Earthquakes.
Dr. Emily’s Professor Architectural Engineering at The University of Cambridge, Noted That Older Buildings Can and Have Been Strengthened, Such Asada and New Zealand.
Prof AMORN PIMARNMAS, President of the Association of Thailand, Said That There Regulations In 43 Provinces on Earthquake-Proofing Buildings, Less Than 10% of Buildings Even Estimated to Be Quake-Resistant.
Yet The Building That Collapsed Was New – In Fact, It Still Under the Earthquake Hit – And The Updated Building Standards Would Have Applied.
Dr Pimarnmas Said Bangkok’s Soft Soil May Have a Part in IT Collapse, As It Can Amplify Ground Motions Three Or Oro Times Over.
He added: “However, there are other assumptions Such material (Concrete and Reinforcements) Quality and Someone In (The) Structural System. These Remain to Be Investigated In Detail.”
Having Studied Video, Dr. Málaga-Chuquitaype Said It Appears a “Flat Slab” Construction Process Was Being – which is no longer recommended in Earthquake-prone Areas.
“A ‘Flat Slab’ System Is A Way of Constructing Buildings Where Floors make to Rest Directly on columns, without using beams,” He explained.
“Imagine A Table Supported Only Legs, With No Extra Horizontal Supports Underneath.
“While this Design has cost and architectural advantages, is performs Poorly During Earthquakes, ofen Failing in A Brittle and Sudden (Almost Explosive) Manner.”
What about The Buildings in Myanmar?
Mandalay in Myanmar Was Much Closer to The Ground Slipped and Would Have Experienced Significantly More Severe Shaking Than Bangkok.
Although Myanmar Earthquakes, Dr Ian Watkinson, A Lecturer in Earth Sciences University, Thought It Was It Were Buildings Were Constructed to Be Earthquake-Proof.
“General Poverty, Major Political, Disasters – Eg The Indian Ocean Tsunami in 2004 – has distracted the country concentrating on the unpredictable risks from Earthquakes,” He said.
“This Means, In Many Cases, Building Design Codes even enforced, and Construction Happens That could be commanded to enhanced seismic Risk, Example Flood Plains and Steep Slopes.”
Parts of Mandalay and Its Buildings Also Lie Along The Floodplain of The Ayerwaddy River. This Makes Them Vulnerable to a Process Called Liquefaction.
This Happens When The Soil has a High water content, and the Shaking Causes The Sediment to Lose Strength and Behave Like a Like. This Increases The Risk of Landslides and Building Collapses, As the Ground Can No Hold Them Up.
Dr So Warned Thnes Of The Further Damage to Buildings Near a Fault Line Due to Aftershocks – Tremors That Follow, Which Can Be Caused By The Sudden Transfer Of Energy Into Nearby Rock.
“Most of the Time Aftershocks Are Smaller Than The Main Shock, and Tend to Decrease in Size and Frequency Over Time,” She Said.






